Calcific Tendinitis
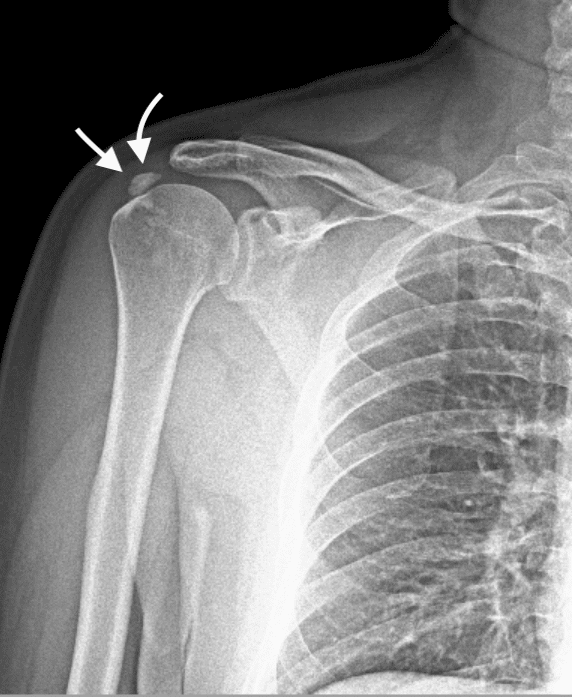
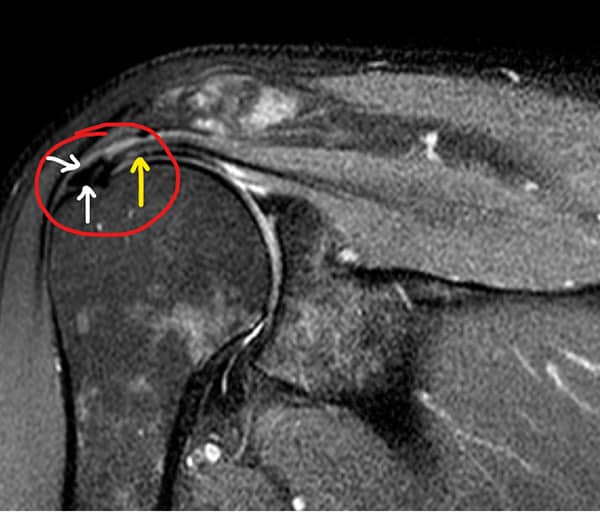
- Calcific tendinitis, also known as calcium deposition, refers to the accumulation of calcium crystals in the shoulder muscles and tendons. It is more commonly seen in women. Factors such as diabetes, goiter, and repetitive or sudden strenuous movements can contribute to its development. Night pain can lead to sleep disturbances and psychological problems, negatively impacting the quality of life. Diagnosis can be made through examination, X-rays, and MRI scans. The severity and duration of symptoms determine the course of treatment, which typically does not involve surgery. Avoiding physical strain helps prevent excessive stress on the tendons. If the pain persists, physical therapy may be added following a cortisone injection in the shoulder. A small group of patients may require surgery, and those who undergo minimally invasive (arthroscopic) treatment often experience significant relief within 3-4 weeks.
Bilgi Havuzu